When you start learning programming, one of the first things that you come across is the JavaScript conditional statement. The conditional statement in JavaScript allows you to make decisions in your program. It helps your code respond differently based on the condition, just like the way you make decisions in life. In this blog, you will understand what conditional statements are, their types, and comparison, with examples in detail.
Table of Contents:
What is Conditional Statement in JavaScript?
A conditional statement in JavaScript is a way to tell the program to execute a particular code only when a specific condition is true. If the condition is false, another block of code will execute depending on the condition. This is how a conditional statement in JavaScript works. A sample JavaScript code is given below so that you can understand it better:
Code:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code is used to check whether the number is greater than, less than, or exactly 0. Based on that, it prints a message whether the number is positive, negative, or zero.
Level Up Your Web Development Career
Learn the technologies behind modern apps and gain the confidence to crack top tech interviews.
Importance of Conditional Statements in JavaScript
- A JavaScript conditional statement helps your program to make decisions instead of executing the whole code in one go.
- With a conditional statement, your code can react differently based on the input, data, or situations of the user.
- These statements help you control the flow of the program and avoid unnecessary actions.
- These statements also help to make your application interactive and user-friendly.
- It also helps you to apply logic, like checking age, login details, scores, or permission, before you perform any action.
- Without using a conditional statement in JavaScript, your program will behave the same way every time, even when the data changes.
- It also makes your code look smarter, more flexible, and closer to real-life decision-making.
Types of Conditional Statements in JavaScript
In this section, we are going to discuss the different types of conditional statements in JavaScript.
1. if Statement in JavaScript
This conditional statement runs a block of code only when the condition given is true. If the condition is false, it skips the code inside the block.
Syntax:
The syntax for the if statement is given below:
if (condition) {
// code will run only if the condition is true
}
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code is used to check if your age is 18 or more. If the condition is true, it prints a message saying that you are eligible to vote.
2. if…else Statement in JavaScript
This conditional statement is used to check a condition and then run a block of code if it is true, and another block if it is false. It allows your program to make decisions between two outcomes.
Syntax:
The syntax for if…else statement is given below:
if (condition) {
// code if the condition is true
} else {
// code if the condition is false
}
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above code is used to check if the age is 18 or above. If it is above 18, it prints that you can vote. If it is not, it tells you that you are not eligible to vote.
3. if…else if…else ladder in JavaScript
You can use this conditional statement when you have to check multiple conditions one after another. If the condition is true, that particular block runs, and the rest are skipped.
Syntax:
The syntax for if…else if…else ladder in JavaScript is given below:
if (condition1) {
// code
} else if (condition2) {
// code
} else {
// code
}
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code is used to check your marks and then compares them with different ranges of grades. Based on the score, it prints Grade A, B, C, or fail.
4. Nested if…else Statements in JavaScript
You can use the nested if…else statements in JavaScript when one condition depends on another. You have to place an if…else block inside another if…else block to check more specific conditions.
Syntax:
The syntax for a nested if-else statement in JavaScript is given below:
if (condition1) {
if (condition2) {
// code if both conditions are true
} else {
// code if condition1 is true but condition2 is false
}
} else {
// code if condition1 is false
}
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code is used to check if you are 18 or older. If you are, then it checks if you have an ID. If yes, you are allowed to enter; otherwise, you are asked for an ID.
5. Switch Statement in JavaScript
The switch statement in JavaScript allows you to compare one value against multiple values. It helps to keep your code clean and easier to read than multiple if…else statements in JavaScript.
Syntax:
The syntax for the switch statement in JavaScript is given below:
switch (expression) {
case value1:
// code
break;
case value2:
// code
break;
default:
// code if no case matches
}
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code is used to check the value of the variable named day and match it with the given cases. Depending on the day, it prints a message, and if it does not match any case, it shows a default message.
6. Ternary Operator in JavaScript
It is the shortest form of a JavaScript conditional statement. It is used to make simple decisions in one line using a question mark “?”.
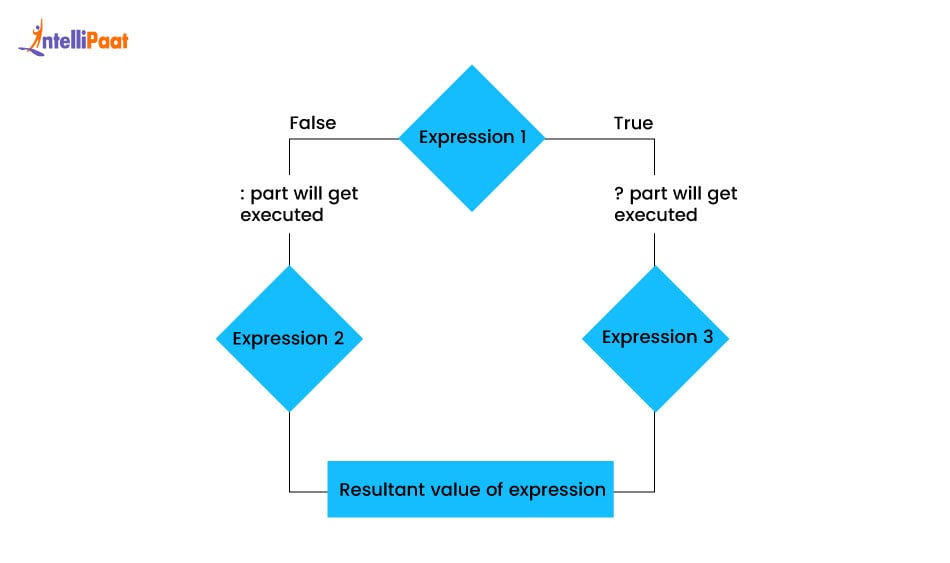
Syntax:
The syntax for the ternary operator in JavaScript is given below:
condition ? expressionIfTrue : expressionIfFalse;
Example:
Output:
Explanation: The above JavaScript code shows a short way to write a JavaScript conditional statement. It is used to check a condition. If the condition is true, it runs the first expression. If the condition is false, it runs the second one.
Comparison of Conditional Statements in JavaScript
Here is a comparison table between the different types of conditional statements in JavaScript.
| Conditional Statement |
What It Does |
Best Used When |
Example Use Case |
| if |
Checks a condition and runs code only if it’s true |
You have just one condition to test |
Check if the age is above 18 |
| if…else |
Runs one block of code if the condition is true, else runs another |
You want two possible outcomes |
Show login success or failure |
| if…else if…else |
Checks multiple conditions one after another |
You need more than two options |
Assign grades based on marks |
| Nested if…else |
One if statement inside another if or else |
You want to check a condition inside another condition |
Check age first, then check ID |
| switch |
Compares one value against different cases |
You have many fixed values to compare |
Display a message based on the day of the week |
| Ternary Operator (?:) |
Short form of if…else in one line |
You want a quick, simple decision |
Assign a message based on age |
Common Mistakes of JavaScript Conditional Statements
Some common mistakes while using conditional statements in JavaScript are given below:
1. Many beginner programmers confuse the assignment operator (=) with the comparison operators (==) or (===) in a conditional statement. The == operator compares values after type coercion, whereas the === operator compares both value and type without performing type conversion.
2. Not using braces in conditional statements can give unexpected results, especially when you add more lines of code in the future.
3. In a switch statement, if you forget to write break, the code does not stop and keeps running the next cases even after a match is found.
4. Sometimes, a conditional statement contains logically inconsistent conditions, such as if (x < 10 && x > 20), which can never be true. In such cases, you should use the OR (||) operator when checking mutually exclusive ranges.
5. In a conditional statement in JavaScript, if you forget to add an else or default block, then it may leave some cases unnoticed. This makes the program do nothing.
Best Practices for Using JavaScript Conditional Statements
Some best practices for using JavaScript conditional statements are given below:
1. You should always use strict comparison operators like === so that you can avoid unexpected results that are caused by type conversion.
2. You should always write conditions that are short and easy to understand instead of writing long and confusing conditions.
3. Instead of using many if…else if conditional statements, you should use switch to make your code look cleaner and more readable.
4. You should always handle the “what if nothing matches” situation using else or default to avoid any missing outputs.
5. You should use the ternary operator to make small decisions, but you should avoid it for long or complex logic.
Real-World Applications of JavaScript Conditional Statements
Some real-world applications of JavaScript Conditional Statements are given below:
1. Conditional statements are used in login and authentication systems to check if the username and password are correct and then allow or deny access.
2. Many e-commerce websites use conditional statements in JavaScript to apply discounts if the user has a coupon or if the total price of the product is over a certain amount.
3. When someone submits a form, the conditional statements are used to check if fields like email, name, and password are entered properly.
4. Many weather apps use conditional statements to show messages like “It’s hot outside” or “Carry an umbrella if it’s raining”.
5. Conditional statements are also used for game development to check if the player scored points, lost lives, or won the game.
Conclusion
JavaScript conditional statements help your code decide what to do next based on the situation. Once you understand how to use conditional statements properly, you will be able to build smarter and more interactive websites and applications that are responsive. These statements play a major role in making your programs work the right way, like checking user input, showing or hiding content, or making logical choices. Therefore, you need to keep practicing different types of conditional statements in JavaScript to enhance your coding skills.
Upskill today by enrolling in our Full Stack Development Course. Also, prepare for your next interview with our JavaScript Interview Questions, prepared by industry experts.
JavaScript Conditional Statements – FAQs
Q1. Can I use multiple conditions in one JavaScript conditional statement?
Yes, you can use logical operators like && (and) and | | (or) to check more than one condition at a time.
Q2. What happens if I don’t write an else or default statement?
If no condition matches and no else/default is provided, nothing executes inside that conditional block, and program flow continues normally.
Q3. Are switch statements faster than if...else statements?
Both these statements work at the same speed. But using switch would be a better choice if you have too many fixed values to check.
Q4. Can I use a ternary operator inside another ternary operator?
Yes, you can. But it is not recommended because it makes your code hard to read and understand.
Q5. Do JavaScript conditional statements work in both browsers and Node.js?
Yes, they work the same in both environments. This is because they are part of core JavaScript.